Chemical Force Microscopy
–Chemical functionalization of AFM tip for molecular recognition and nanolithography–
1. Temporaly and spatially controlled surface oxidation by AFM tip functionalized with photocatalyst C60
AFM tip was chemically functionalized by a tripod-C60 molecule and subjected to the surface oxidation reaction. Under visible light irradiation, oxidative damage of substrate DNA origami on mica surface was cuccessfully observed in a single molecular level.
Funding sources: ETH Grants, SNF
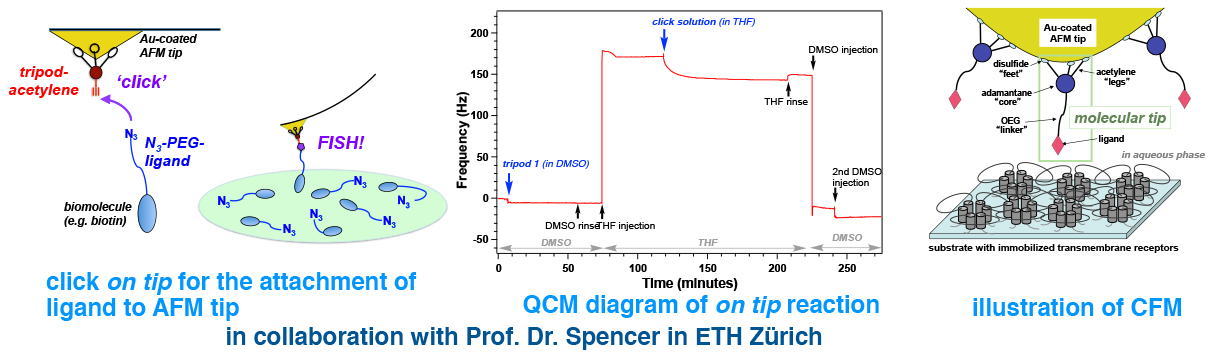
Collaborators: Prof. Dr. Nic Spencer (ETH), Prof. Dr. Antonella Rossi (University of Cagliari)
Publications: ACS Nano 2021.
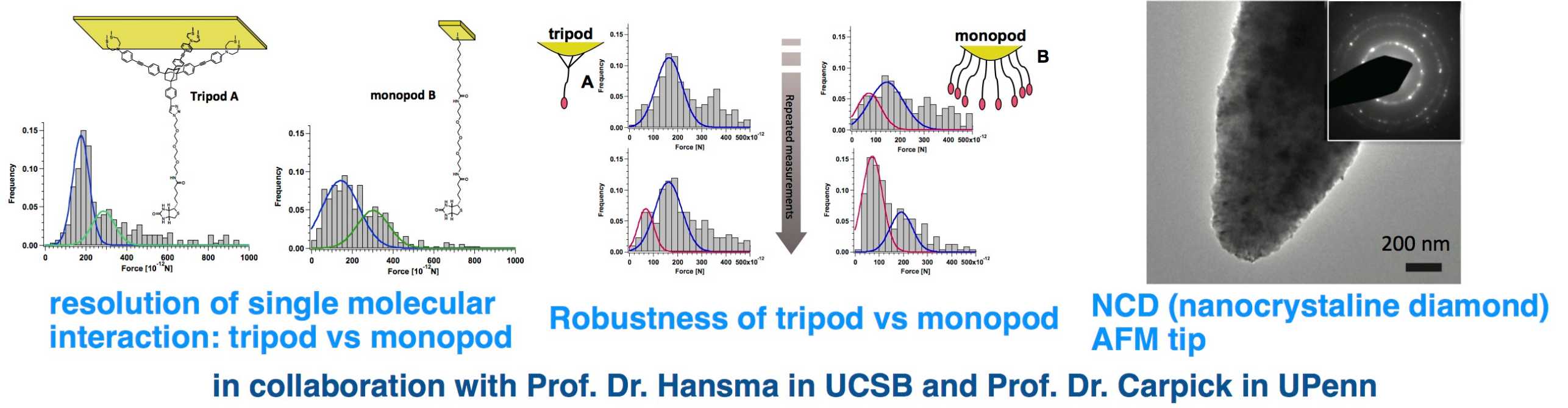
2. Molecular recognition by AFM in a single molecular level
Many biologically important proteins are transmembrane receptors, which are difficult to express in quantity and to crystalize. AFM analysis, which is also amenable to the measurements under physiological condition, is an ideal way of mechanism analyses such transmembrane receptors. Unique molecular tripods were synthesized to successfully observe single molecular ligand–receptor interactions. In addition to the Au-coated AFM tips, nano-crystalline diamond (NCD) AFM tips were used addressing super-robust chemical tips.
Funding sources: University of Pennsylvania Nano-Bio Interface Center (NSF), SNF, ETH Grants
Collaborators: Prof. Dr. Helen Hansma (University of California at Santa Barbara), Prof. Dr. Rob Carpick (University of Pennsylvania)
Publications: Langmuir 2010, J. Mat. Chem. 2012.
3. Analyzing the transmembrane receptors by AFM
A recombinant of P2X2 receptor, transmembrane ATP receptor involved in pain transmission, was prepared and immobilized on mica surface. AFM imaging in solution revealed a channel-like structure ,suggesting the protein formed 3D structures on surface. Further efforts using other transmembrane receptors are currently going on.
Funding Sources: ETH Grants, Nanomedicine grants (Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan)
Collaborators: Dr. Ken-ichi Nakazawa (NIHS, Japan), Prof. Dr. Nic Spencer (ETH)
Publications: Nanoscale 2015, Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005.
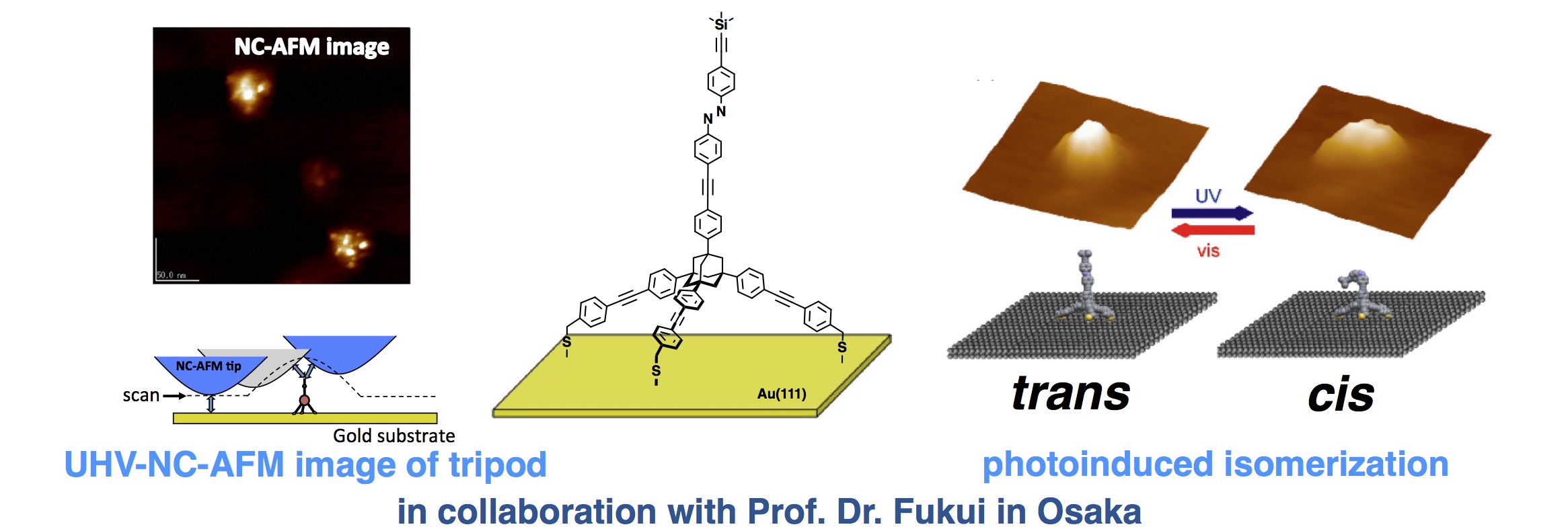
4. Photoswitchable molecular tripod for AFM tip
In order to realize a simultaneous bifunctional AFM imaging (topography and chemical identification), a unique photo-switchable molecular tripod was designed and synthesized. The molecule remained stably attached to the gold surface and showed reversible photoinduced E and Z isomerization as observed by UHV-NC-AFM.
Funding Sources: Nanomedicine project (Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan), SNF
Collaborators: Prof. Dr. Ken-ichi Fukui (Osaka University)
Publications: Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006.