In vivo Imaging
–Investigating Biological Function by in vivo Imaging–
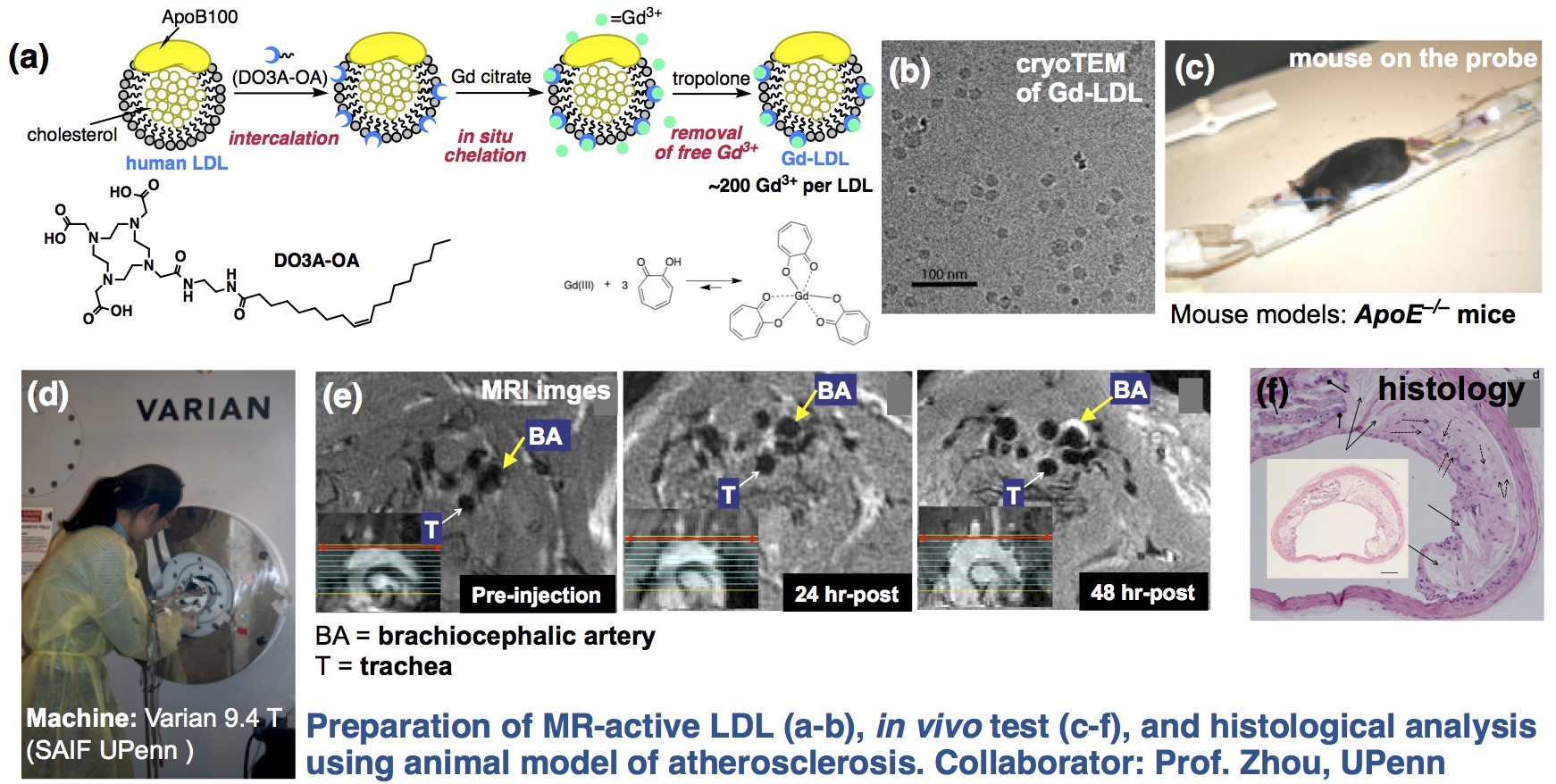
1. Development of MRI contrast agents for efficient and selective detection of atherosclerosis
In order to detect the early stage of atherosclerosis, natural low-density lipoprotein (nLDL) – isolated from human blood – was functionalized by Gd3+ chelate and injected to an apoE–/– knockout mouse. We were happy to see very bright enhancement in vivo. The current efforts of our study is on totally synthetic LDL (sLDL) using lipid nanoparticle formation, ligation reactions and peptide chemistry.
Funding Sources: American Heart Association, ETH Grant, JST PRESTO, SNF
Collaborators: Prof. Dr. Rong Zhou (University of
Pennsylvania), Prof. Dr. Eva Toth (CRNS Orleans), Prof. Dr. Garret A.
FitzGerald (University of Pennsylvania)
Publications: ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science 2025, Chem. Sci. 2020, Langmuir 2018, Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, Chem. Commun. 2011.
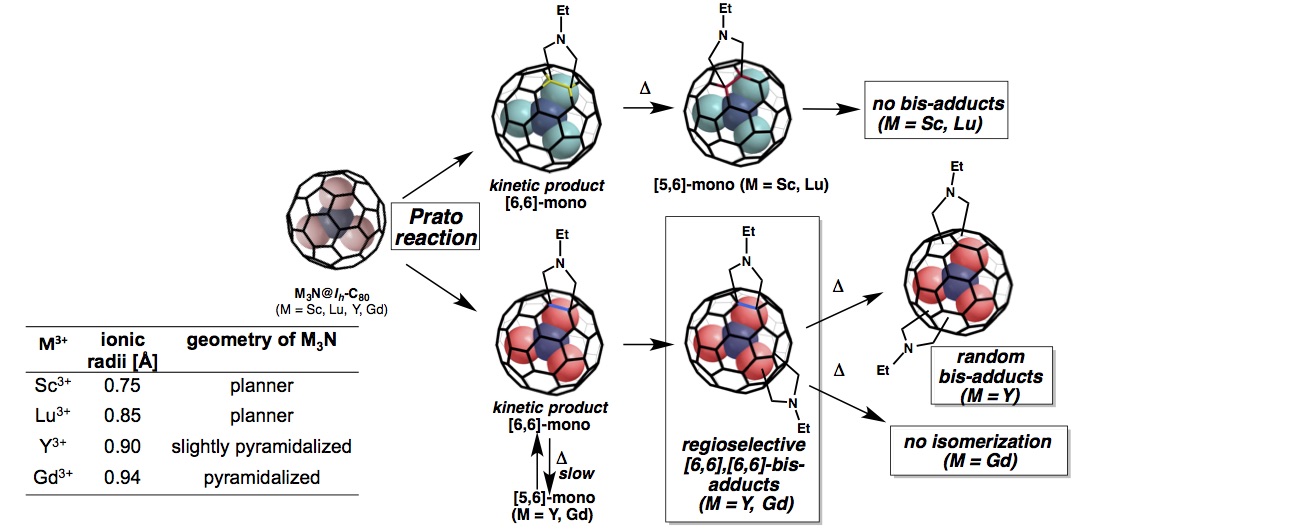
2. Super-efficient Gd3N@C80-based MRI contrast agents
Along with avoiding problematic side-effects of Gd3+chelate-based MRI contrast agents – which are in clinical use – Gd@fullerene-based compounds are a promising core for bright MRI contrast agents. We are excited by the design and synthesis of new Gd@fullerene derivatives with the aim of producing super-efficient contrast agents. Currently, the chemical reactivity of Gd3N@C80 are under investigation.
Funding Sources: SNF, ETH grants
Collaborators: Prof. Dr. Silvia Osuna (University of Girona), Prof. Dr. Steven Stevenson (Purdue University at Fort Wayne)
Publications: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, Chem. Eur. J. 2014, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012.
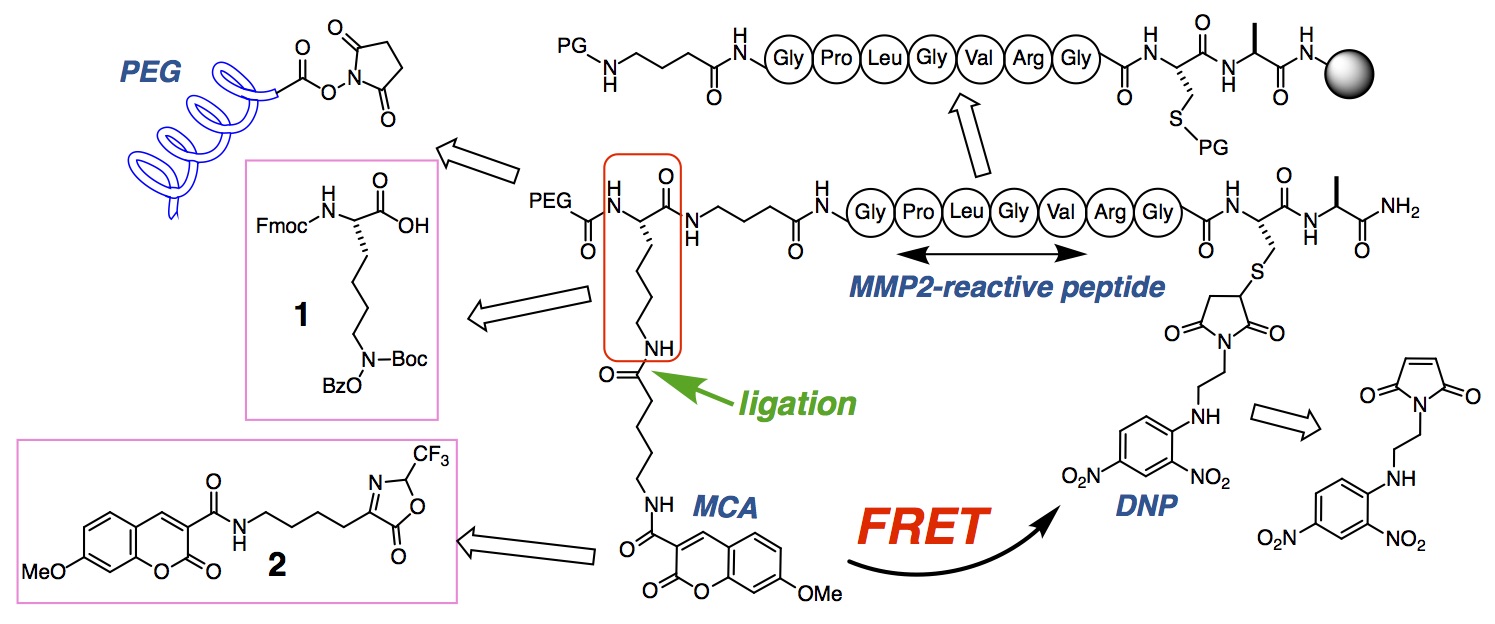
3. MMP-responsive optical probes for the detection of malignant diseases
To elucidate mechanistic apporoaches of identifying vulnerable atherosclerosis and malignant cancers, and to differentiate this type by in vivo imaging, MMP-specific imaging probes are under development. Our first probe was based on FRET imaging and was selectively activatable by MMP2. Other types of probes are currently under investigation.
Funding Sources: American Heart Association, SNF, ETH grants
Collaborators: Prof. Dr. Martin Baumgartner (University of Zurich Children's Hospital), Dr. Sung-Sik Lee (ETH, ScopeM)
Publications: Small 2025, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017.